This demo will focus on pipelines combining the following AWS service for translating video speech and analysing sentiment and key-words in speech.
- AWS Transcribe: automatic speech recognition (speech to text)
- AWS Polly: Convert text to life like speech
- AWS Translate: Translate text from one lang to another
- AWS Comprehend: Analysis of text data e.g. sentiment analysis, POS tagging, key phrases, entity detection
The architecture diagram for this workflow is shown below. An mp3 file will be uploaded to S3 and a step function workflow will execute tasks listed above to transcribe, translate and convert text back to speech, which will be stored in mp3 format in S3. We will also invoke a lambda function as one of the tasks to parse the transcribed data so it is in the required format for the downstream tasks. Outputs from most of the tasks will stored in S3, whilst lambda logs will automatically stored in cloudwatch logstream.  The code for the following exercise can be found in the github repository here and For the next sections, we need to install the dependencies in the pipfile by following the instructions here
The code for the following exercise can be found in the github repository here and For the next sections, we need to install the dependencies in the pipfile by following the instructions here
The environment can then be activated by running the following commands from the root of the repository.
1
2
$ export PYTHONPATH=.
$ pipenv shell
Loading data into S3
The mp3 file we want to use is stored here and is just some speech in english about Machine Learning. We first need to create a bucket in S3 awstestnlp and then copy this data over, either via console or using cli as below
shell $ aws s3 cp datasets/nlp/source/transcribe-sample.mp3 s3://awstestnlp/source/transcribe-sample.mp3
The architecture diagram shows a lambda function being invoked after the AWS transcribe is called to parse the output of the transcribed data stored in S3. The parsed data will then be passed to the next stage in the state machine for further analysis by other AWS services. In the next section we will deploy the code to lambda function for parsing the data.
Deploying lambda function
We will first need to create a lambda function containing the following handler.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
s3 = boto3.resource("s3")
obj = s3.Object(event["BucketName"], event["TranscribeOutputKey"]).get()
big_str = json.loads(obj["Body"].read().decode("utf-8"))
transcribed_text = big_str["results"]["transcripts"][0]["transcript"]
print(transcribed_text)
return {"TranscribedText": transcribed_text}
To deploy the lambda, we can either do this directly in the console or by using zip archives with no dependencies. The following script from the base of the repository creates a zip archive and deploys the function code to lambda.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
import boto3
import shutil
import json
import click
from pathlib import Path
import os
iam_client = boto3.client("iam")
lambda_client = boto3.client("lambda")
@click.command()
@click.option("--function_name", help="Name of lambda resource to create")
@click.option(
"--role", default="ReadObjectsS3forLambda", help="IAM role name for lambda resource"
)
@click.option("--timeout", default=20, help="Max allowable timeout for lambda")
def create_lambda_aws(
function_name, role, timeout, handler="lambda_function.lambda_handler"
):
os.chdir(Path(__file__).parent)
shutil.make_archive(function_name, "zip", function_name)
with open(f"{function_name}.zip", "rb") as f:
lambda_zip = f.read()
role = iam_client.get_role(RoleName=role)
print(f"\n Role details: {json.dumps(role, default=str)} \n")
response = lambda_client.create_function(
FunctionName=function_name,
Runtime="python3.9",
Role=role["Role"]["Arn"],
Handler=handler,
Code=dict(ZipFile=lambda_zip),
Timeout=timeout, # Maximum allowable timeout
)
print(json.dumps(response, indent=4, default=str))
if __name__ == "__main__":
create_lambda_aws()
The script above also assumes we have a Lambda execution role already created to include a policy to peform s3:GetObject action in the S3 bucket and log to Cloudwatch.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "logs:CreateLogGroup",
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:us-east-1:376337229415:*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:logs:us-east-1:376337229415:log-group:/aws/lambda/parseS3json:*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::*"
}
]
}
By default, it uses a role named “ReadObjectsS3forLambda” for the lambda resource to assume. If we need to change this, we can pass in an additional parameter, when running this via the cli. If doing this via the console, just select the correct execution role. The timeout setting defaults to 20 seconds, which can also be overwritten by passing the argument in the cli (from the console, this can be set directly to a maximum of 15 minutes)
1
$ python lambdas/deploy_lambda_function.py --function_name parses3json --role "NewLambdaRole" --timeout 150
Step Function Execution
Before creating and executing the Step Functions workflows, first need to grant Step Functions workflow (state machine) permissions to trigger Lambda functions via IAM role as below. Here I have attached a number of AWS managed policies to the role to allow access to translate, comprehend, polly, transcribe, comprehend services and S3,lambda etc

If creating new step function, the create_state_machine method of boto sfn client requires the Amazon States Language definition of the state machine in string format as described here This is already defined in the json file for the Step Function to orchestrate the NLP services and Lambda.
To create and execute the step function, execute the script from the command line as below. This will first deploy the step function and attach role ‘StepFunctionAWSNLPServices’, with step function name ‘NLPExecution’. This script will use the state machine definition from file named AWSNLPServicesdefinition.json. Once deployed the step function will execute and translate the source mp3 video (default lang ‘en-us’) to spanish (set by --target_lang_code). This needs to be paired with a voice-id for the chosen target language, required by AWS Polly (see [AWS docs] for voice id choices (https://docs.aws.amazon.com/polly/latest/dg/voicelist.html)). This will translate the video to spanish based on the target language specified.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
$ python projects/nlp/execute_pipeline.py --sf_name NLPExecution --target_lang_code es --voice_id Lupe --deploy --role StepFunctionAWSNLPServices
Deploying step function:
{
"stateMachineArn": "arn:aws:states:us-east-1:376337229415:stateMachine:NLPExecution",
"creationDate": "2022-05-13 03:13:49.982000+01:00",
"ResponseMetadata": {
"RequestId": "10cea0a5-1a75-4d31-b59c-527e78fcb566",
"HTTPStatusCode": 200,
"HTTPHeaders": {
"x-amzn-requestid": "10cea0a5-1a75-4d31-b59c-527e78fcb566",
"date": "Fri, 13 May 2022 02:13:50 GMT",
"content-type": "application/x-amz-json-1.0",
"content-length": "117"
},
"RetryAttempts": 0
}
}
waiting for 30 secs for deployment to complete and state function in active state
Step function NLPExecution is active with resource arn: arn:aws:states:us-east-1:376337229415:stateMachine:NLPExecution
Executed state machine NLPExecution:
{
"executionArn": "arn:aws:states:us-east-1:376337229415:execution:NLPExecution:9f572dda-0707-4851-b5c9-21496931b874",
"startDate": "2022-05-13 03:47:00.646000+01:00",
"ResponseMetadata": {
"RequestId": "7cdd8471-670f-42ad-8f6b-1a9a95b610fe",
"HTTPStatusCode": 200,
"HTTPHeaders": {
"x-amzn-requestid": "7cdd8471-670f-42ad-8f6b-1a9a95b610fe",
"date": "Fri, 13 May 2022 02:47:00 GMT",
"content-type": "application/x-amz-json-1.0",
"content-length": "145"
},
"RetryAttempts": 0
}
}
Execution status is 'RUNNING', waiting 10 secs before checking status again
Execution status is 'RUNNING', waiting 10 secs before checking status again
Execution status is 'RUNNING', waiting 10 secs before checking status again
Execution status is 'RUNNING', waiting 10 secs before checking status again
Job succeeded !
The input payload to the state machine execution above is automatically passed in the following format when the script execute_pipeline.py is run.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
{
"BucketName": "awstestnlp",
"Source": "s3://awstestnlp/source/en-US/transcribe-sample.mp3",
"TranscribeOutputKey": "transcribe/es/transcribed.json",
"PollyVideoOutputKey": "polly/es/Lupe/",
"PollyResponseOutputKey": "polly/es/response.json",
"ComprehendOutputKey": "comprehend/es/text_analysis.json",
"SourceLanguageCode": "en-US",
"TargetLanguageCode": "es",
"JobName": "Test",
"VoiceId": "Lupe",
"EngineType": "neural",
"SkipComprehend": false
}
If the step function is already created, we can execute it by passing the –no-deploy argument to the command above.
1
$ python projects/nlp/execute_pipeline.py --sf_name NLPExecution --target_lang_code es --voice_id Lupe --no-deploy
We can see from the flow below, that depending on the engine type detected, the input will go to the respective task to execute - which sets the engine parameter to ‘neural’ or ‘standard’ depending on the voice id chosen from thislist Also, there is another choice task to determine whether to skip the comprehend step if the language is not one of the following (de”, “pt”,”en”,”it”,”fr”,”es”) as the others are not supported by all the services e.g. syntax detection It uses the $.SkipComprehend state variable which is part of the input passed to the state machine (above) and computed in the code in execute_pipeline.py
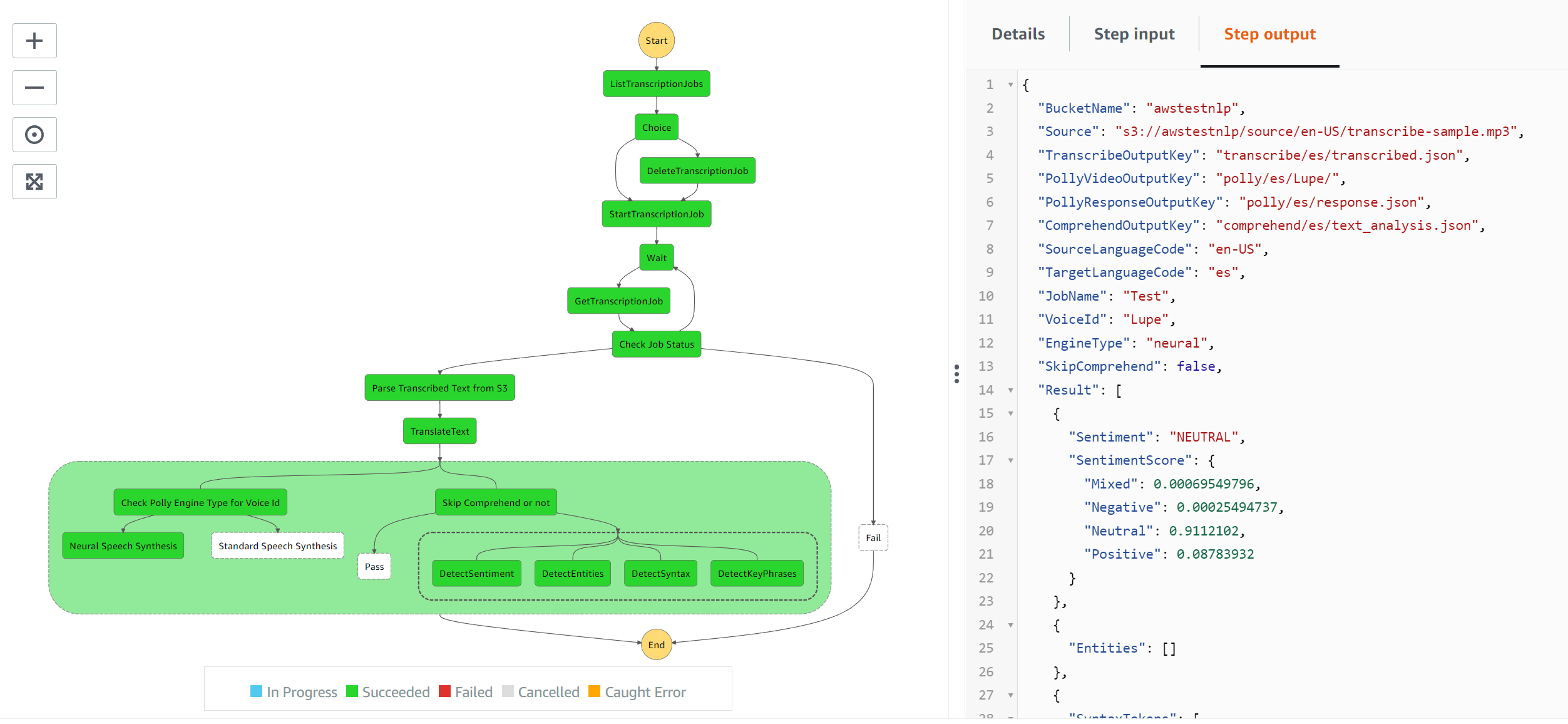
The following execution translates to French using voice id ‘Mathieu’. This is a standard engine and the flow passes it ot the appropriate task. Since French is supported by all comprehend services, the parallel block is executed.
1
$ python projects/nlp/execute_pipeline.py --sf_name NLPExecution --target_lang_code fr --voice_id Mathieu --no-deploy
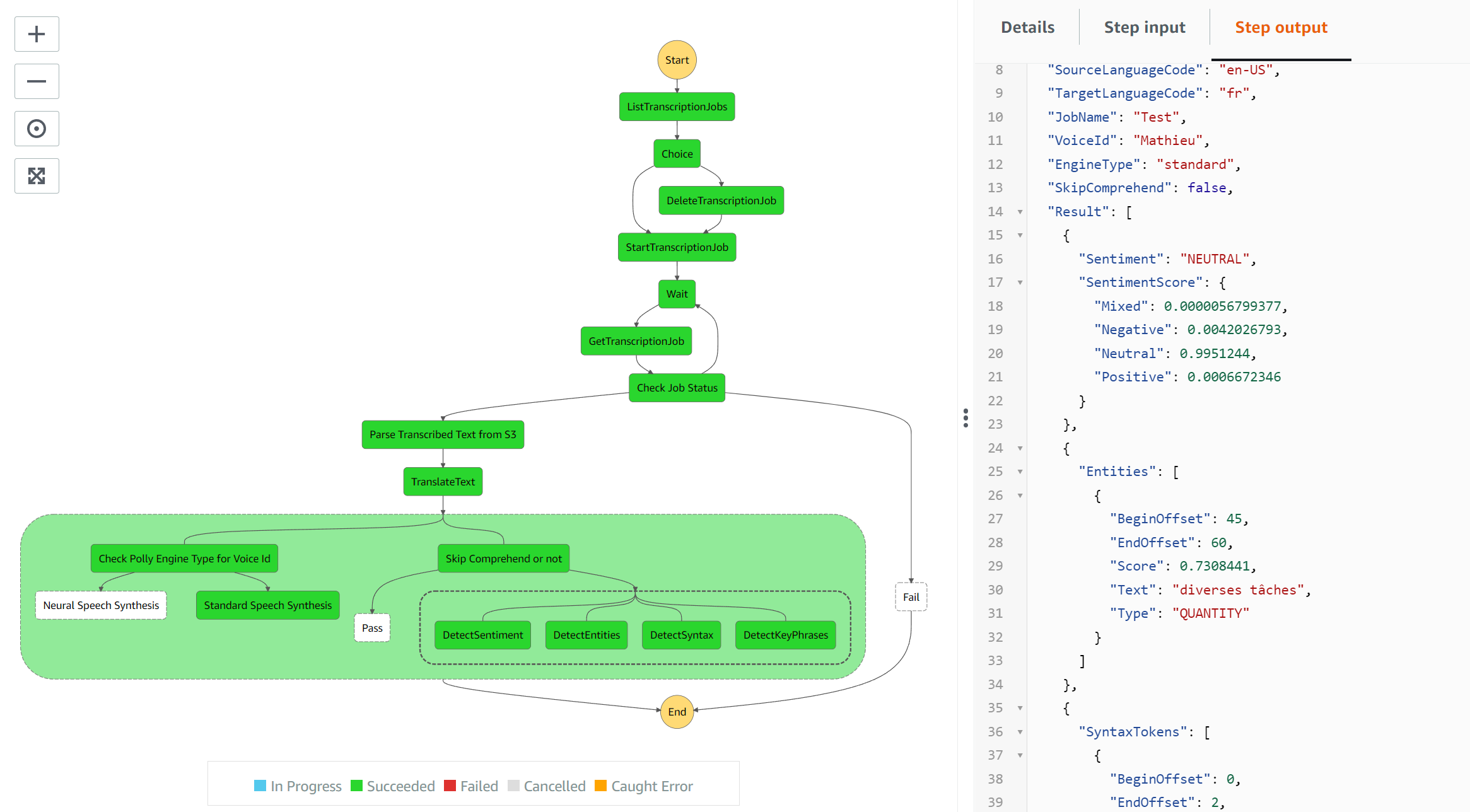
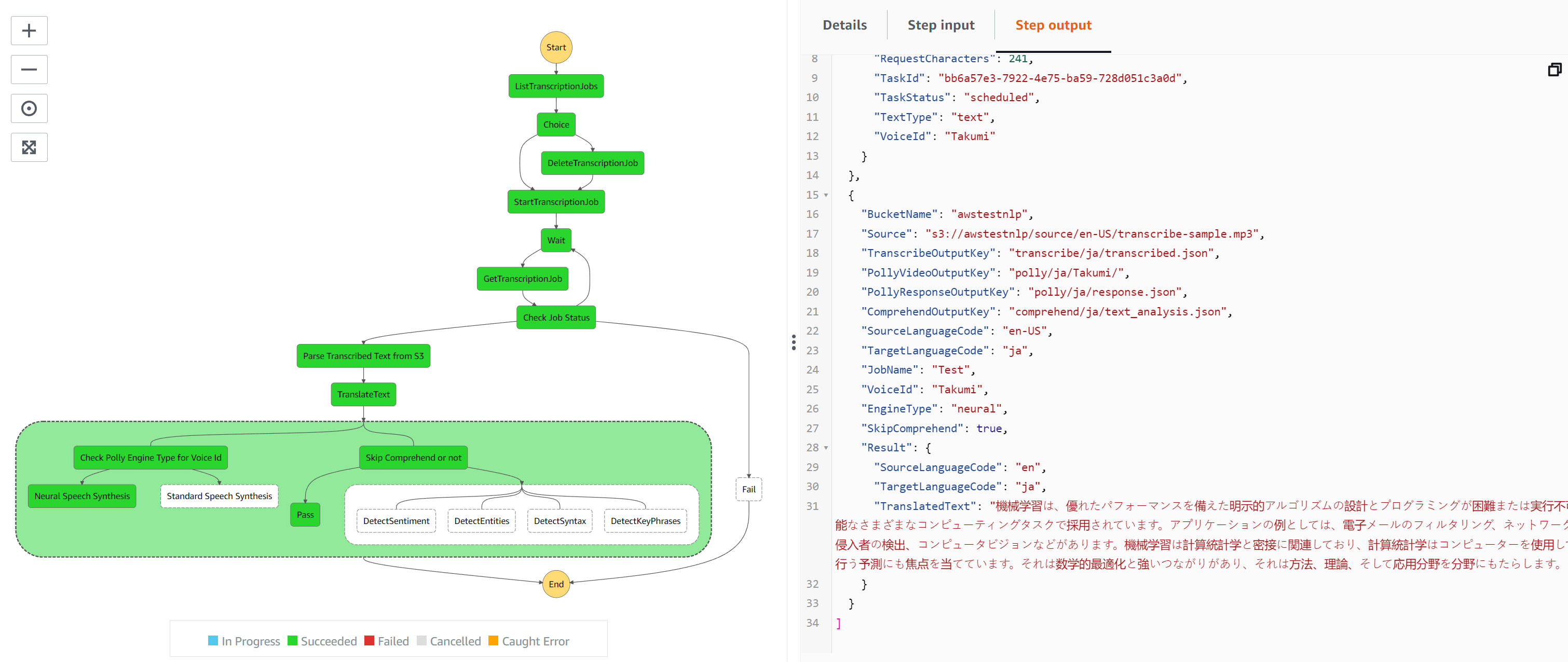
This execution translates to Japanese using voice id ‘Takumi’. This is a neural engine. However, the language is not supported by all the AWS Comprehend services used in the state machine and hence the choice task will skip this
1
$ python projects/nlp/execute_pipeline.py --sf_name NLPExecution --target_lang_code ja --voice_id Takumi --no-deploy
Copying results to local
To copy all the contents of the s3 bucket awstetsnlp to a local foldes
1
$ aws s3 cp s3://awstestnlp datasets/nlp --recursive
The outputs of the steps from step functions can be accessed in this folder including the translations of speech in different languages here

Comments powered by Disqus.